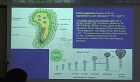
We explored the correlations of the excitation energy transfer network (EET-NET) structure of photosystem II (PSII) core complex (Protein Data Bank 1W5C) in Thermosynechococcus elongates. We regard main pigements − chlorophylls and pheophytins − a...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.
https://www.riss.kr/link?id=T13246619
- 저자
-
발행사항
서울 : 성균관대학교 일반대학원, 2013
-
학위논문사항
학위논문(석사) -- 성균관대학교 일반대학원 , 에너지과학과 , 2013. 8
-
발행연도
2013
-
작성언어
영어
- 주제어
-
발행국(도시)
서울
-
형태사항
71 ; 26 cm
-
일반주기명
지도교수: 안태규
- DOI식별코드
- 소장기관
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
We explored the correlations of the excitation energy transfer network (EET-NET) structure of photosystem II (PSII) core complex (Protein Data Bank 1W5C) in Thermosynechococcus elongates. We regard main pigements − chlorophylls and pheophytins − and EET rates (EET-RATE) between two main pigments as nodes and links of the established network, respectively. Here we estimated EET-RATE by a simple dipole-dipole approximation (Förster theory) using on the coordination and spatial orientation of photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophylls and pheophytins in PSII core (EET-dynamics; EET-DYN). In this work we ignored other photosynthetic pigments like carotenoids and quinones, rather we concentrated on the EETs among main pigments in PSII core. Using the network analysis of EET-NET, we constructed the simplified (rather arbitrary) network model and explored the question how much of excited energy in chlorophylls could reach to the reaction centers. We focus on the following network parameters: degree centrality (DC), betweenness centrality (BC), and the clustering coefficient (CC) originated from the theoretical network analysis. Our simulation results show the close correlations between chlorophyll network properties and functionality. Specifically they also show the functionality of individual pigments of special pairs in the EET-DYN with EET-NET. The special pair chlorophylls (node 11, 12 and 21, 22 for D1 and D2 proteins, respectively) in the reaction center (RC) are characterized by a high BC and a low CC. Remarkably chlorophylls in active branch (node 11, 21) has even larger BC than those in inactive branch (node 12, 22) of the PSII core. This simulation results imply that chlorophylls in active branch (node 11, 21) can deliver more excitation energy to reaction centers with high probability than those in the other branch of special pair. In this work, we found that several significant principles of EET-DYN network in whole PSII core complex can be even re-emphasized in our simplified network of EET-NET. This network can be applicable to analyze the functionality of the EET-DYN in PSII core and the mathematical topology of chlorophyll pigments in EET-NET.
목차 (Table of Contents)
- I. Background
- 1. Network Theory
- 1.1. Basic Concepts of Network Theory
- 1.2. Network Characteristics
- 1.2.1. Degree Centrality
- I. Background
- 1. Network Theory
- 1.1. Basic Concepts of Network Theory
- 1.2. Network Characteristics
- 1.2.1. Degree Centrality
- 1.2.2. Betweenness Centrality
- 1.2.3. Clustering Coefficient
- 1.3. Tools
- 1.3.1. Networkx (Python)
- 1.3.2. Gephi
- 2. Overview of the PSII Complex
- 2.1. Composition of PSII complex
- 2.2. Reaction Center
- 3. Energy Transfer Theory
- 3.1. Förster Theory
- 3.2. Excitation Energy Transfer Model
- II. Method
- 1. Sample Preparation
- 2. Excitation Energy Transfer Rate Calculation
- 3. Simplified EET-NET Construction
- 4. Algorithm of Energy Distribution
- 5. Parameter for the Functionality
- 6. Pearson Correlation
- III. Results
- 1.Monomer Case
- 1.1. Degree Centrality
- 1.2. Betweenness Centrality
- 1.3. Clustering Coefficient
- 2. Dimer Case
- 2.1. Degree Centrality
- 2.2. Betweenness Centrality
- 2.3. Clustering Coefficient
- IV. Conclusion
- References
- Appendix
- Summary