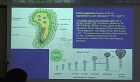
흰쥐 입천장발생은 배자 발생 14일에서 17일까지 입천장선반 (palatal shelves)이 아래쪽으로 성장하고 16일에 혀 위쪽으로 이동하여 중앙을 중심으로 병합하여 17일에는 완전한 입천장이 형성된...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.

흰쥐에서 임신 중 레티노산이 입천장 형태발생에 미치는 영향 = Effect of Retinoic Acid on Palate Formation during Rat Embryogenesis
한글로보기https://www.riss.kr/link?id=A77005064
- 저자
- 발행기관
- 학술지명
- 권호사항
-
발행연도
2006
-
작성언어
-
-
주제어
입천장발생 ; 입천장갈림증 ; 레티노산 ; 배자 발생 ; 형태형성 ; Hox 유전자 ; 세포사멸 ; Cleft palate ; Embryogenesis ; Hox gene ; Palatogenesis ; Pattern formation ; Programmed cell death ; Retinoic acid
-
KDC
510
-
등재정보
KCI등재후보,ESCI
-
자료형태
학술저널
-
수록면
331-341(11쪽)
-
KCI 피인용횟수
1
- 제공처
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
국문 초록 (Abstract)
흰쥐 입천장발생은 배자 발생 14일에서 17일까지 입천장선반 (palatal shelves)이 아래쪽으로 성장하고 16일에 혀 위쪽으로 이동하여 중앙을 중심으로 병합하여 17일에는 완전한 입천장이 형성된다. 레티노산은 비타민 A의 생체 내 활성 대사산물로써 발생에서 배자의 앞뒤축 형성 등에 관여하는데, 이런 레티노산에 과다히 노출∙결핍 시에는 기형이 유발되고, 배자 축 형성에 관여하는 Hox 유전자의 발현 또한 조절한다고 알려져 있다.
본 연구는 임신중 레티노산이 입천장 형태발생에 미치는 영향을 보기위하여 임신 11일째 흰쥐에 레티노산을 복강내주사로 주입하고 발생 13일부터 17일까지의 배자를 분리한 후 배자의 형태를 분석하고 또 형태형성에 관여하는 Hox와 Bcl-2 family 유전자를 포함하여 레티노산에 의해 차등 발현하는 유전자를 (DD) RT-PCR방법을 이용하여 분석하였다.
실험 결과 레티노산에 노출된 실험군 배자의 경우 정상군에 비해 머리 발생 지연을 포함하여 머리-엉덩 길이와 사지 등의 길이가 짧았다. 또 발생 17일째에는 정상군에서는 완전한 입천장이 형성되었으나 실험군에서는 총 52예의 배자 중 36예에서 입천장갈림증이 관찰되었으며, 입천장갈림증 간격은 약 0.80±0.36 mm이었다.
DDRT-PCR 결과 레티노산 투여로 인해 차등발현하는 유전자들이 많이 존재함이 관찰되었다. Hoxa7 유전자는 정상군에서는 발생 13일째에 그러나 레티노산 투여군에서는 발생 15일째에 강하게 발현한 후 점차 감소한 반면 Hoxc8은 발현이 거의 감지되지 않았으나 정상군에서는 발생 16일째에서 그리고 레티노산 투여군에서는 15일째에서 아주 약한 발현이 감지되었다. Bcl-2 family 유전자의 경우 정상군에서는 발생 13일에서 17일까지 Bclxl과 Bcl-2 유전자, 그리고 Bax 유전자 모두 강하게 발현하였으나, 실험군의 경우 Bcl-xl과 Bcl-2의 발현이 발생 16일 이후에는 감소한 반면 Bax의 경우는 발생 13일에서 15일까지 매우 저하되었다.
이상의 결과로 임신중 레티노산 노출이 배자 발생과정 중 입천장갈림증을 포함한 형태적 기형유발을 가능하게 하는 물질임을 알 수 있었으며, 또 배자의 형태 발생에 관련된 Hox 유전자와 세포사멸 관련 유전자인 Bcl-xl, Bcl-2, 그리고 Bax 유전자의 발현을 조절하여 배자, 특히 입천장의 형태 기형 유발에 관여한 것으로 유추된다.
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
In order to understand the effect of retinoic acid (RA) on the craniofacial pattern formation during embryogenesis, we injected RA intraperitoneally into the pregnant female rat on day 11 post coitum (p.c.) and then embryos of day 13 to day 17 p.c. we...
In order to understand the effect of retinoic acid (RA) on the craniofacial pattern formation during embryogenesis, we injected RA intraperitoneally into the pregnant female rat on day 11 post coitum (p.c.) and then embryos of day 13 to day 17 p.c. were isolated consequently. The overall morphology and the differential gene expression patterns were analyzed by the microscopic and (DD) RT-PCR methods, respectively.
For the morphological study, the retardation of craniofacial region, the shortage of crown rump length and limbs
were analyzed in the RA-treated embryos. In the RA-treated embryos of day 17, it was observed that the palatogenesis was completely finished just like in the normal embryos. However, the cleft plate was observed in 36 out of 52 total samples with the distance of cleft palate being 0.80±0.36 mm in average. The temporal expression pattern of Hox genes through RT-PCR revealed that the expression of Hoxa7 reached its peak on day 13 then slowly declined in the normal embryos. Whereas in the RA-treated embryos, the expression peak was observed on day 15, then declined subsequently. With the Hoxc8 gene, its expression was low in all stages until the day 16 of normal embryogenesis. On the other hand, Hoxc8 gene expression was detected slightly early on day 15 in the RA-treated embryos. In the study of Bcl-2 family genes, uniformly strong expression of anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic genes was observed from day 13 to day 17 of normal embryos, whereas anti-apoptotic gene expressions were decreased after day 16 in the RAtreated embryos. Additionally, a dramatic decline of pro-apoptotic gene expression was observed from day 13 to day 15 of the RA-treated embryos.
Therefore, we believe that RA is a potential factor that is actively involved in the cleft palate formation. Moreover, it is profoundly linked with the regulation of Hox and Bcl-2 family gene expression pattern that leads to the embryonic malformation.
참고문헌 (Reference)
1 "Vitamin A deficiency in the late gastrula stage rat embryo results in a one to two vertebral anteriorization that extends" 257 : 14-29, 2003
2 "The identification of Hoxc8target genes" 102 : 2420-2424, 2005
3 "Teratogenicity of retinoic acid" 62 : 178-180, 2000
4 "Retinoids and Hox genes" 10 : 969-978, 1996
5 "Retinoicacid induces apoptosis-associated neural differentiation of amurine teratocarcinoma cell line" 70 : 47-58, 1998
6 "Retinoic acid가 흰쥐의 구개 발생 중 세포증식능과 Fibroblast growth factor 2 Fibroblast growthfactor receptor 2의 발현에 미치는 영향" 34 : 41-55, 2001
7 "Retinoic acid response element in HOXA-7 regulatory regionaffects the rate not the formation of anterior boundaryexpression" 46 : 325-328, 2002a
8 "Retinoic acid and retinoic acid receptors in craniofacial development." 8 : 437-443, 1997
9 "Programmedcell death is required for palate shelf fusion andis regulated by retinoic acid" 245 : 145-156, 2002
10 "Programmed cell death is not anecessary prerequisite for fusion of the fetal mouse palate" 48 : 39-46, 2004
1 "Vitamin A deficiency in the late gastrula stage rat embryo results in a one to two vertebral anteriorization that extends" 257 : 14-29, 2003
2 "The identification of Hoxc8target genes" 102 : 2420-2424, 2005
3 "Teratogenicity of retinoic acid" 62 : 178-180, 2000
4 "Retinoids and Hox genes" 10 : 969-978, 1996
5 "Retinoicacid induces apoptosis-associated neural differentiation of amurine teratocarcinoma cell line" 70 : 47-58, 1998
6 "Retinoic acid가 흰쥐의 구개 발생 중 세포증식능과 Fibroblast growth factor 2 Fibroblast growthfactor receptor 2의 발현에 미치는 영향" 34 : 41-55, 2001
7 "Retinoic acid response element in HOXA-7 regulatory regionaffects the rate not the formation of anterior boundaryexpression" 46 : 325-328, 2002a
8 "Retinoic acid and retinoic acid receptors in craniofacial development." 8 : 437-443, 1997
9 "Programmedcell death is required for palate shelf fusion andis regulated by retinoic acid" 245 : 145-156, 2002
10 "Programmed cell death is not anecessary prerequisite for fusion of the fetal mouse palate" 48 : 39-46, 2004
11 "Palatogenesisand potential mechanisms for clefting" 45 : 351-358, 2000
12 "Nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in China: assessment of candidate regions." 38 : 149-156, 2002
13 "Nonsyndromic cleft lip and palate: complex genetics and environmental effects" 65 : 505-515, 2001
14 "Induction of cell-cycle arrest by all-trans retinoic acid in mouse embryonic palatal mesenchymal (MEPM) cells" 83 : 349-354, 2005
15 "Identification of a mechanism tolocalize generation of retinoic acid in rat embryos" 69 : 155-167, 1997
16 "Hox geneactivation by retinoic acid" 329-334, 1991
17 "Homeotic transformations of murine vertebraeand concomitant alteration of Hox codes induced by retinoicacid" 89-104, 1991
18 "Homeotic transformation of the occipital bones of the skullby ectopic expression of a homeobox gene" 835-359 841, 1992
19 "Function of vitamin A in vertebrate embryonic development" 131 : 705-708, 2001
20 "Effects ofretinoic acid on the neural crest-controlled organs of fetalrats" 19 : 355-358, 2003
21 "Ectopic expression of Hox-2 3 induces craniofacial and skeletalmalformations in transgenic mice" 3-16, 1992
22 "Dose-response for retinoic acid-induced forelimb malformations and cleft palate: a comparison of computerized image analysis and visual inspection." 71 : 289-295, 2004
23 "Craniofacial abnormalitiesinduced by ectopic expression of the homeobox gene Hox-1 1 in transgenic mice" 337-347, 1989
24 "Craniofacial abnormalities induced by the ectopic expressionof homeobox genes" 396 : 97-112, 1997
25 "Connected to death: the (unexpurgated) mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis." 310 : 66-67, 2005
26 "Cleft lip and palate incidenceamong the live births in the Republic of Korea" 17 : 49-52, 2002b
27 "Candidate genes for nonsyndromic cleft lip and palate" 68 : 272-279, 2001
28 "Bax translocates from cytosol to mitochondria incardiac cells during apoptosis development of a GFP-BaxstableH9c2 cell line for apoptosis analysis" 289 : 477-487, 2005
29 "Annealingcontrol primer system for improving specificity of PCRamplification" 35 : 1180-1184, 2003
30 "Analysis of plausibledownstream target genes of Hoxc8 in F9 teratocarcinomacells" 30 : 141-148, 2003
31 "Alterations in apoptosis andepithelial-mesenchymal transformation in an in vitro cleftpalate model" 113 : 907-914, 2004
32 "2 gene results in developmentalabnormalities" 323-2 336, 1992
동일학술지(권/호) 다른 논문
-
Serially Sectioned and Segmented Images of the Mouse for Learning Mouse Anatomy
- 대한해부학회
- 박진서(Jin Seo Park)
- 2006
- KCI등재후보,ESCI
-
Up-regulation of PSD-95 in the Rat Hippocampal Formation after Chronic Renal Failure
- 대한해부학회
- 정용욱(Yong-Wook Jung)
- 2006
- KCI등재후보,ESCI
-
흰쥐 뇌하수체에서의 NCX와 NCKX isoform mRNA의 발현에 관한 연구
- 대한해부학회
- 조미행(Mi Haeng Cho)
- 2006
- KCI등재후보,ESCI
-
중간대뇌동맥과 심장동맥에서 죽상경화증 양상과 Angiopoietin-2 발현의 비교
- 대한해부학회
- 신은경(Eun Kyung Shin)
- 2006
- KCI등재후보,ESCI
분석정보
인용정보 인용지수 설명보기
학술지 이력
| 연월일 | 이력구분 | 이력상세 | 등재구분 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 평가예정 | 계속평가 신청대상 (계속평가) | |
| 2020-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보학술지 선정 (신규평가) |  |
| 2019-12-01 | 평가 | 등재후보 탈락 (계속평가) | |
| 2018-12-01 | 평가 | 등재후보로 하락 (계속평가) |  |
| 2015-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2011-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2010-02-02 | 학술지명변경 | 한글명 : 대한해부학회지 -> Anatomy and Cell Biology외국어명 : The Korean Journal of Anatomy -> Anatomy and Cell Biology |  |
| 2008-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 선정 (등재후보2차) |  |
| 2007-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보 1차 PASS (등재후보1차) |  |
| 2006-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보로 하락 (등재유지) |  |
| 2004-01-01 | 평가 | 등재 1차 FAIL (등재유지) |  |
| 2001-07-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 선정 (등재후보2차) |  |
| 1999-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보학술지 선정 (신규평가) |  |
학술지 인용정보
| 기준연도 | WOS-KCI 통합IF(2년) | KCIF(2년) | KCIF(3년) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
| KCIF(4년) | KCIF(5년) | 중심성지수(3년) | 즉시성지수 |
| 0.1 | 0.09 | 0.223 | 0.03 |




 스콜라
스콜라