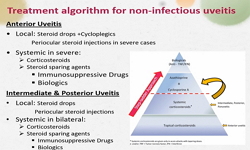
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a common complication of diabetes mellitus. The prevalence of neuropathic pain is estimated to occur in about 30-50% of all diabetic patients. Clinical symptoms vary depending on the nerves affected, and may inc...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.
https://www.riss.kr/link?id=A100768276
- 저자
- 발행기관
- 학술지명
- 권호사항
-
발행연도
2015
-
작성언어
-
- 주제어
-
KDC
500
-
등재정보
KCI등재후보
-
자료형태
학술저널
- 발행기관 URL
-
수록면
277-281(5쪽)
-
KCI 피인용횟수
4
- DOI식별코드
- 제공처
- 소장기관
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a common complication of diabetes mellitus. The prevalence of neuropathic pain is estimated to occur in about 30-50% of all diabetic patients. Clinical symptoms vary depending on the nerves affected, and may include both positive and negative symptoms. Many patients with DPN experience pain or discomfort, anxiety, depression, and limitations in activity, which can significantly impact their physical, emotional, and social well-being. Early diagnosis is essential for the successful management of DPN. Routine management consists of glucose and risk factor control, and symptomatic relief, along with therapies designed to target the underlying disease pathology. Pharmacological treatment of DPN includes tricyclic compounds, serotonin noradrenalin reuptake inhibitors, the antioxidant α-lipoic acid, anticonvulsants, opiates, membrane stabilizers, topical capsaicin, and other drugs. Management of DPN must be tailored to each individual, and depends on a variety of factors, including disease severity and response to treatment. (Korean J Med 2015;89:277-281)
참고문헌 (Reference)
1 Tesfaye S, "Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy" 352 : 341-350, 2005
2 Berger A, "Use of tricyclic antidepressants in older patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy" 23 : 251-258, 2007
3 Ziegler D, "Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a meta-analysis" 21 : 114-121, 2004
4 Ziegler D, "Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy: Update 2006" 1084 : 250-266, 2006
5 Keen H, "Treatment of diabetic neuropathy with gamma-linolenic acid. The gamma-Linolenic Acid Multicenter Trial Group" 16 : 8-15, 1993
6 Hollingshead J, "Tramadol for neuropathic pain" CD003726-, 2006
7 McCleane G, "Topical application of doxepine hydrochloride, capsaicin and a combination of both produces analgesia in chronic human neuropathic pain; a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study" 49 : 574-579, 2000
8 Tesfaye S, "The prevalence of diabetic neuropathy and its relation to glycaemic control and potential risk factors: the EURODIAB IDDM Complications Study" 39 : 1377-1384, 1996
9 Dyck PJ, "The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study" 43 : 817-824, 1993
10 Jensen MP, "The impact of neuropathic pain on health-related quality of life: review and implications" 68 : 1178-1182, 2007
1 Tesfaye S, "Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy" 352 : 341-350, 2005
2 Berger A, "Use of tricyclic antidepressants in older patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy" 23 : 251-258, 2007
3 Ziegler D, "Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a meta-analysis" 21 : 114-121, 2004
4 Ziegler D, "Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy: Update 2006" 1084 : 250-266, 2006
5 Keen H, "Treatment of diabetic neuropathy with gamma-linolenic acid. The gamma-Linolenic Acid Multicenter Trial Group" 16 : 8-15, 1993
6 Hollingshead J, "Tramadol for neuropathic pain" CD003726-, 2006
7 McCleane G, "Topical application of doxepine hydrochloride, capsaicin and a combination of both produces analgesia in chronic human neuropathic pain; a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study" 49 : 574-579, 2000
8 Tesfaye S, "The prevalence of diabetic neuropathy and its relation to glycaemic control and potential risk factors: the EURODIAB IDDM Complications Study" 39 : 1377-1384, 1996
9 Dyck PJ, "The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study" 43 : 817-824, 1993
10 Jensen MP, "The impact of neuropathic pain on health-related quality of life: review and implications" 68 : 1178-1182, 2007
11 Boulton AJ, "The global burden of diabetic foot disease" 366 : 1719-1724, 2005
12 Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, "The effect of intensive diabetes therapy on the development and progression of neuropathy" 122 : 561-568, 1995
13 Valk GD, "The assessment of diabetic polyneuropathy in daily clinical practice:reproducibility and validity of Semmes Weinstein monofilaments examination and clinical neurological examination" 20 : 116-118, 1997
14 Dyck PJ, "Signs and symptoms versus nerve conduction studies to diagnose diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy: Cl vs. NPhys trial" 42 : 157-164, 2010
15 Candrilli SD, "Prevalence and the associated burden of illness of symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and diabetic retinopathy" 21 : 306-314, 2007
16 Kim SS, "Prevalence and clinical implications of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: results from a nationwide hospital-based study of diabetic neuropathy in Korea" 103 : 522-529, 2014
17 Rosenstock J, "Pregabalin for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy:a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial" 110 : 628-638, 2004
18 Sindrup SH, "Pharmacologic treatment of pain in polyneuropathy" 55 : 915-920, 2000
19 Dworkin RH, "Pharmacologic management of neuropathic pain: evidence-based recommendations" 132 : 237-251, 2007
20 Ziegler D, "Oral treatment with a-lipoic acid improves symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy – The SYDNEY 2 trial" 29 : 2365-2370, 2006
21 Gaede P, "Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes" 348 : 383-393, 2003
22 Inzucchi SE, "Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach. Position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD)" 35 : 1364-1379, 2012
23 Boulton AJ, "Guidelines for the diagnosis and outpatient management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy" 15 : 508-514, 1998
24 Rose MA, "Gabapentin: pharmacology and its use in pain management" 57 : 451-462, 2002
25 Backonja M, "Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus; a randomized controlled trial" 280 : 1831-1836, 1998
26 Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group, "Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes" 358 : 2545-2559, 2008
27 Chong MS, "Diabetic painful neuropathy: current and future treatment option" 67 : 569-585, 2007
28 Vinik AI, "Diabetic neuropathies" 43 : 957-973, 2000
29 Gore M, "Burden of illness in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy:the patients’ perspectives" 7 : 892-900, 2006
30 Boulton AJ, "American Diabetes Association. Diabetic neuropathies: a statement by the American Diabetes Association" 28 : 956-962, 2005
31 Finnerup NB, "Algorithm for neuropathic pain treatment: an evidence based proposal" 118 : 289-305, 2005
32 Dworkin RH, "Advances in neuropathic pain: diagnosis, mechanisms, and treatment recommendations" 60 : 1524-1534, 2003
동일학술지(권/호) 다른 논문
-
동맥색전술로 치료된, 내시경적점막절제술에 의한 거대 위 벽내 혈종
- 대한내과학회
- 박진주 ( Jin Ju Park )
- 2015
- KCI등재후보
-
- 대한내과학회
- 곽혜빈 ( Hye Bin Gwag )
- 2015
- KCI등재후보
-
신경섬유종증에서 갈색세포종의 영향으로 발생된 뇌동맥류 파열 1예
- 대한내과학회
- 권민관 ( Min Kwan Kwon )
- 2015
- KCI등재후보
-
터너증후군 환자의 대동맥 축착증을 스텐트 삽입술로 치료한 증례 1예
- 대한내과학회
- 박승운 ( Seung Woon Park )
- 2015
- KCI등재후보
분석정보
인용정보 인용지수 설명보기
학술지 이력
| 연월일 | 이력구분 | 이력상세 | 등재구분 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 평가예정 | 계속평가 신청대상 (계속평가) | |
| 2021-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보학술지 선정 (신규평가) |  |
| 2018-12-01 | 평가 | 등재후보 탈락 (계속평가) | |
| 2017-12-01 | 평가 | 등재후보로 하락 (계속평가) |  |
| 2013-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2010-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2008-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2006-05-15 | 학술지명변경 | 외국어명 : Korean Journal of Medicine -> The Korean Journal of Medicine |  |
| 2006-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) |  |
| 2003-01-01 | 평가 | 등재학술지 선정 (등재후보2차) |  |
| 2002-01-01 | 평가 | 등재후보 1차 PASS (등재후보1차) |  |
| 2000-07-01 | 평가 | 등재후보학술지 선정 (신규평가) |  |
학술지 인용정보
| 기준연도 | WOS-KCI 통합IF(2년) | KCIF(2년) | KCIF(3년) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| KCIF(4년) | KCIF(5년) | 중심성지수(3년) | 즉시성지수 |
| 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.259 | 0.02 |





 KCI
KCI KISS
KISS