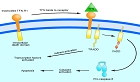
위암 세포의 생존 기전을 조사하기 위하여 SNU-1, SNU-16, SNU-620 위암 세포주들을 사용한 비교 연구를 실시하였다. 흥미롭게도 SNU-620 세포는 SNU-1과 SNU-16 세포들에 비하여 anti-Fas, H_(2)O_(2), etoposide...
http://chineseinput.net/에서 pinyin(병음)방식으로 중국어를 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환된 중국어를 복사하여 사용하시면 됩니다.
- 中文 을 입력하시려면 zhongwen을 입력하시고 space를누르시면됩니다.
- 北京 을 입력하시려면 beijing을 입력하시고 space를 누르시면 됩니다.
위암 세포에서 Bcl-w의 발현, 세포 사멸 억제 기능 및 그 작용 기전 = Bcl-w supresses gastric cancer cell death blocking SAPK/JNK activation
한글로보기https://www.riss.kr/link?id=T8617595
- 저자
-
발행사항
서울 : 연세대학교 대학원, 2003
- 학위논문사항
-
발행연도
2003
-
작성언어
한국어
-
주제어
위암 ; 세포 사멸 ; cell death ; gastric adenocarcinoma ; Bcl-w ; SAPK ; JNK
-
KDC
513.99434 판사항(4)
-
발행국(도시)
서울
-
형태사항
iii, 43p. : 삽도 ; 26 cm.
-
일반주기명
지도교수: 김호근
- 소장기관
-
0
상세조회 -
0
다운로드
부가정보
국문 초록 (Abstract)
위암 세포의 생존 기전을 조사하기 위하여 SNU-1, SNU-16, SNU-620 위암 세포주들을 사용한 비교 연구를 실시하였다. 흥미롭게도 SNU-620 세포는 SNU-1과 SNU-16 세포들에 비하여 anti-Fas, H_(2)O_(2), etoposide, serum withdrawl과 같은 다양한 사멸 자극들에 저항함이 관찰되어 이러한 현상의 기전을 탐구하고자 하였다. 먼저, DNA microarray assay를 수행한 결과 SNU-620은 SNU-1에 비하여 c-met proto-oncogene을 포함한 114개의 유전자를 상대적으로 많이 발현함이 확인되었다. c-met의 이러한 발현 양상은 Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)에 의해서도 다시 한번 확인되었으나 SNU-16 세포에 c-met의 ligand인 Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)의 처리는 anti-Fas, H_(2)O_(2), etoposide, serum withdrawl의 모두에 대한 세포 보호 효과를 유도하지 않았다. 따라서, c-met이 이 모든 자극들에 대하여 SNU-620을 보호하는 인자는 아니라고 생각되었다. 그러한 인자를 확인하기 위한 또 다른 방법으로, anti-Fas, H_(2)O_(2), etoposide, serum withdrawl이 위암 세포를 사멸하는 기전을 조사하였다. 그 결과 이러한 자극들 모두 stress activated protein kinase/c-Jun NH_(2) terminal kinase (SAPK/JNK)를 통하여 위암 세포의 사멸을 유도함이 확인되었다. Bcl-2가 SAPK/JNK의 활성화를 억제할 수 있다는 기존의 보고에 근거해서 SNU-16과 SNU-620에서 Bcl-2 family protein들의 발현 양상을 western blotting으로 비교하였다. 그 결과 Bad, Bak, Bax, Bid, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL의 발현 정도는 SNU-16, SNU-620에서 별다른 차이가 없었으나 유독 Bcl-w만이 SNU-16보다 SNU-620에서 높은 발현을 보였다. 또한 Bcl-w를 SNU-16에 과발현했을 때는 anti-Fas, H_(2)O_(2), etoposide, serum withdrawl에 의한 SAPK/JNK의 활성화 및 세포 사멸이 감소됨이 관찰되었다. 따라서 Bcl-w가 실제로 위암 환자에서도 발현되는지를 조사하기 위하여 다섯 명의 advanced gastric adenocarcinoma (AGC) 환자로부터 획득한 조직을 면역 화학 염색으로 분석하였다. 이 모든 환자에서 Bcl-w는 정상 세포에서는 발현되지 않았지만 두 case에서는 암 세포 특이적으로 발현됨이 관찰되었다. 이 모든 연구 결과를 종합하면 Bcl-w가 위암 세포주 및 위암 환자에서 발현될 수 있는 하나의 생존 인자라고 생각된다.
다국어 초록 (Multilingual Abstract)
To determine a cellular factor supporting the survival of gastric cancer cells, a comparative study was performed using three human adenocarcinoma cell lines, SNU-1, SNU-16 and SNU-620. SNU-620 cells were significantly less susceptible than SNU-1 and ...
To determine a cellular factor supporting the survival of gastric cancer cells, a comparative study was performed using three human adenocarcinoma cell lines, SNU-1, SNU-16 and SNU-620. SNU-620 cells were significantly less susceptible than SNU-1 and SNU-16 to various lethal stimuli including anti-Fas, H_(2)O_(2), etoposide, and serum withdrawal. DNA microarray analyses revealed that 114 genes were expressed in SNU-620 cells to relatively higher levels than in SNU-1 cells. c-met proto-oncogene was one such gene. While the higher expression of c-met in SNU-620 cells was further confirmed by a RT-PCR analysis, it was found that c-met was not such a component that can protect the gastric cancer cells from all the tested stimuli. Interestingly, anti-Fas, H_(2)O_(2), etoposide, and serum withdrawal were found to kill SNU-16 cells by activating SAPK/JNK. The activation of SAPK/JNK was not efficiently induced in SNU-620 cells, suggesting that these cells expressed a protein that can interfere with the SAPK/JNK activation. Given that Bcl-2 can suppress the SAPK/JNK activation under other experimental conditions, the levels of various Bcl-2 family members in SNU-620 and SNU-16 cells were compared by Western blot analysis. While these cells expressed Bad, Bak, Bax, Bid, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL to almost equal levels, the levels of Bcl-w were significantly higher in SNU-620 than SNU-16 cells. Moreover, elevation of the Bcl-w levels in SNU-16 cells by its stable transfection attenuated both the SAPK/JNK activation and cell death induced by all the tested stimuli. These results suggest that the susceptibility of gastric cancer cells to death stimuli is determined, at least in part, by levels of Bcl-w that suppresses the cell death by blocking the SAPK/JNK activation. To explore whether Bcl-w is expressed in patients, tumor specimens were obtained from 5 consecutive cases of advanced gastric adenocarcinomas. An immunohistochemical analysis showed that Bcl-w was expressed in the cancer cells, but not in neighboring normal mucosa, of 2 cases. The sum of the data suggest that Bcl-w can be expressed not only in gastric cancer cell lines but also in AGC patents, and is important for the survival of gastric cancer cells.
목차 (Table of Contents)
- 차례 = i
- 그림 및 표 차례 = ii
- 국문요약 = 1
- I. 서론 = 3
- II. 재료 및 방법 = 7
- 차례 = i
- 그림 및 표 차례 = ii
- 국문요약 = 1
- I. 서론 = 3
- II. 재료 및 방법 = 7
- 1. 세포, 항체 및 시약 = 7
- 2. 세포 배양, transfection 및 처리 = 7
- 3. 세포 사멸 측정 = 8
- 4. Reverse Transcription - Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) 분석 = 8
- 5. Western blot analysis = 9
- 6. In vitro kinase assay = 10
- 7. 면역 조직 화학 염색 = 10
- 8. DNA microarray assay = 11
- III. 결과 = 12
- 1. 사멸 자극들에 대한 위암 세포주들의 반응도 비교 = 12
- 2. DNA microarray assay를 통한 유전자 발현 비교 = 12
- 3. c-met의 기능 분석 = 12
- 4. 위암 세포주에서 Bcl-w의 발현 및 기능 = 13
- 5. 위암 세포 사멸에서 SAPK/JNK의 역할 = 14
- 6. Bcl-w에 의한 SAPK/JNK의 활성화 억제 = 15
- 7. 위암 환자 조직에서 Bcl-w의 발현 = 16
- IV. 고찰 = 17
- V. 결론 = 20
- 참고문헌 = 33
- 영문요약 = 42